Quantum Computing Explained Simply
Ever heard the term quantum computing and thought, “That sounds complicated”? You’re not alone. Most of us grew up with regular computers—laptops, phones, and tablets—that work just fine. So what’s so different about quantum computers, and why are tech giants like Google, IBM, and Microsoft so excited about them?
What Is Quantum Computing, Really?
Imagine you’re flipping a coin. A regular computer sees the result as either heads (1) or tails (0). That’s the basic language of classical computing—everything is made of bits that are either 1 or 0.
But a quantum computer? It sees the coin mid-air. In quantum language, it’s not just heads or tails—it can be both at once. This idea is called superposition. And it’s what makes quantum computing so powerful.
The Basics:
- Classical Computers use bits (0 or 1).
- Quantum Computers use qubits (0, 1, or both at once).
- More qubits = more computing power.
Why Does This Matter?
Let’s say you’re trying to find the fastest route through a city with 50 different destinations. A normal computer would check every possible path—one by one. That takes forever.

A quantum computer? It can try many paths simultaneously, thanks to superposition and something called entanglement (more on that in a second). It’s like having thousands of alternate realities run at once, just to pick the best outcome.
Real-World Example:
Think of Netflix trying to recommend your next show. With so much data about your preferences, a quantum computer could sort through all the options way faster and more accurately than a regular one.
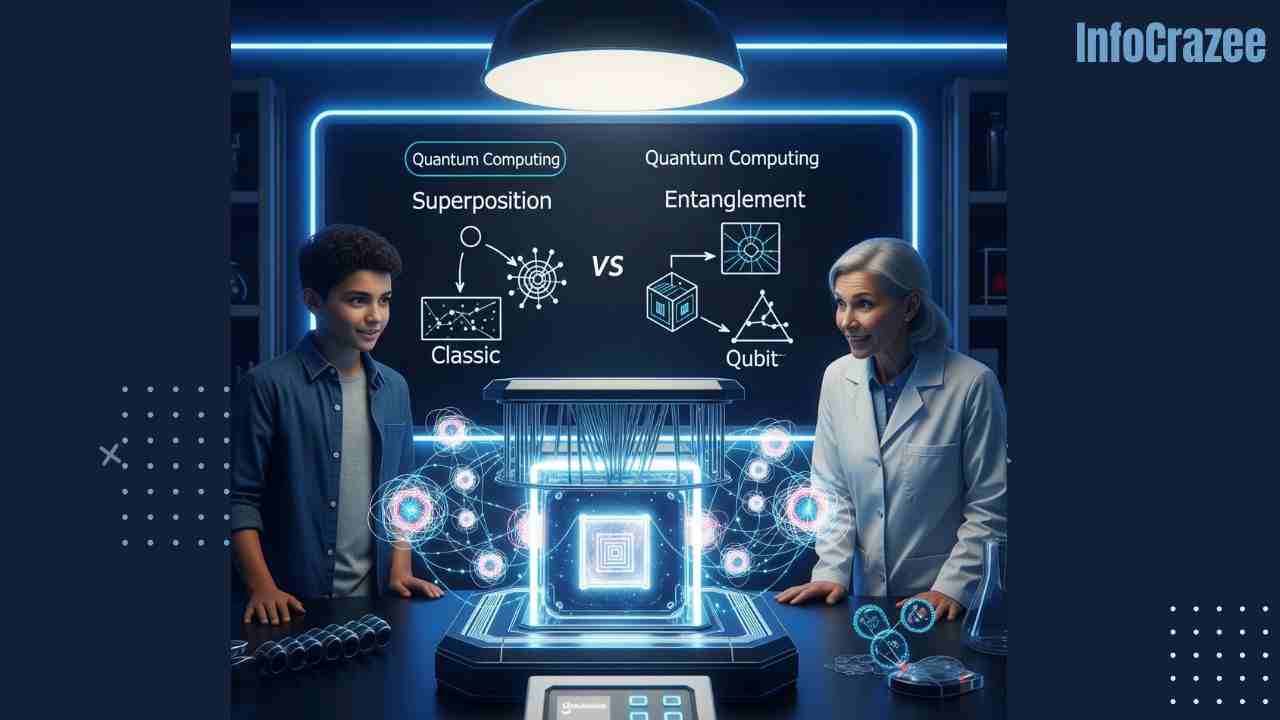
Key Concepts Made Simple
Here are the two most important terms in quantum computing—and how to understand them without a textbook.
1. Superposition
This means a qubit can be in a mix of both 0 and 1 at the same time.
Think of it like: a light switch that’s not just on or off, but also somewhere in between.
2. Entanglement
This means two qubits can be linked so that one affects the other—even if they’re far apart.
Think of it like: twins finishing each other’s sentences, no matter how far they are from each other.
What Can Quantum Computers Do Better?
Right now, classical computers do most tasks perfectly fine. But there are areas where quantum computers could shine:
Possible Uses:
- Medicine: Design new drugs faster by simulating molecules.
- Finance: Analyze markets and spot patterns instantly.
- Climate: Model the planet’s atmosphere in detail to predict weather.
- Cybersecurity: Break (or build) powerful encryption.
They’re not meant to replace your laptop. They’ll mostly work in the background, solving huge problems that today’s computers struggle with.
What’s the Catch?
Quantum computing sounds like magic, but it’s still early days. These computers are:
- Expensive to build
- Delicate—they need near-zero temperatures to work
- Hard to control—tiny errors can mess up the result
Also, we don’t have software that fully uses their power—yet. But companies and researchers are working hard to fix that.
Who’s Working on This?
Lots of big players and startups are in the race, like:
- IBM: Building quantum systems for business and science
- Google: Achieved “quantum supremacy” in 2019
- D-Wave: Focused on solving real-world business problems
- Rigetti: Offers cloud-based quantum tools
Even countries like China, the US, and Europe are investing billions into it.
So Should You Care?
Yes—but don’t panic about your job being replaced by quantum robots (at least not anytime soon!). What matters now is awareness. As quantum tech grows, it’ll affect industries, job markets, and even cybersecurity.
If you’re in tech, science, or business, now’s a good time to start learning the basics. You don’t need to code a quantum program—just knowing the concepts will put you ahead.
Final Thoughts
Quantum computing isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a peek into the future. Like the internet in the 1990s, it’s weird, exciting, and still under construction.
But one day, it might help us cure diseases, protect data, or even find answers to questions we haven’t thought to ask yet.
For now, just knowing how it works—even in a simple way—gives you a front-row seat to one of the biggest tech revolutions of our time.
Curious About What’s Next?
If you found this helpful, here are a few fun options:
- Want to see a quantum computer in action? Check out IBM Quantum Experience (you can play with real quantum circuits online!).
- Follow quantum news from Google AI or Quanta Magazine.
- Keep reading infoCrazee—we’ll keep explaining the future in simple, human terms.
FAQs About Quantum Computing
Q1: Can I use a quantum computer at home?
A: Not yet! They’re still mostly in labs or cloud-based platforms. But you can try simple quantum simulations online through IBM or other tools.
Q2: Is quantum computing dangerous for online security?
A: Eventually, yes—it could break current encryption. But don’t worry; researchers are already working on “quantum-safe” encryption methods.
Q3: Do I need to know physics to understand quantum computing?
A: Nope! If you understand the basic ideas of bits vs. qubits, you’re already ahead of most people. The tech will stay behind the scenes unless you choose to go deeper.