NASA Harnesses Neural Networks to Revolutionize Mars Rover Navigation
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) has announced a groundbreaking advancement in space exploration, integrating advanced neural networks into the navigation systems of its Mars rovers. This cutting-edge AI technology is enhancing the autonomy and efficiency of rovers like Perseverance and Curiosity, enabling them to navigate the rugged Martian terrain with unprecedented precision and independence.
AI-Powered Exploration
The new neural network-based navigation system, dubbed AutoNav 2.0, leverages deep learning to process real-time data from rover cameras and sensors. Unlike traditional navigation systems that rely heavily on pre-programmed routes and Earth-based commands, AutoNav 2.0 allows rovers to autonomously analyze terrain, detect obstacles, and chart optimal paths. This reduces dependency on mission control, cutting communication delays and accelerating exploration.
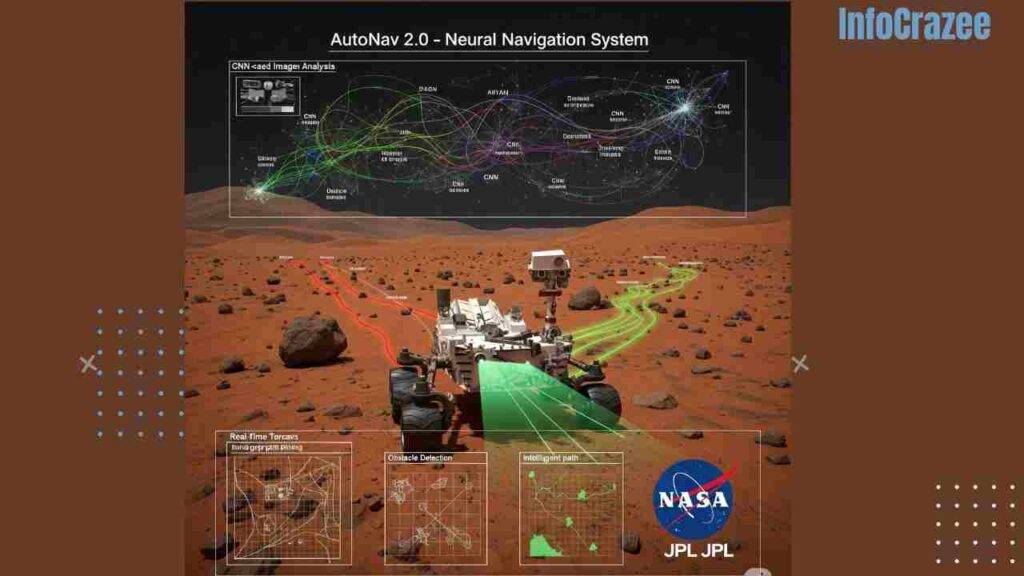
The system uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) trained on vast datasets of Martian imagery and 3D terrain models. These networks enable rovers to identify safe routes, avoid hazards like rocks and steep slopes, and even predict soil stability to prevent getting stuck—a challenge faced by earlier missions. According to JPL’s lead AI researcher, Dr. Emily Chen, “This is like giving the rover a brain to think like a seasoned explorer, making split-second decisions in environments we can’t fully predict from Earth.”
Boosting Mission Efficiency
AutoNav 2.0 has already demonstrated remarkable results. During recent tests, Perseverance covered 30% more ground per sol (Martian day) compared to its previous navigation system, while reducing energy consumption by 15%. The AI’s ability to adapt to dynamic conditions, such as dust storms or shifting dunes, has also minimized wear on rover components, extending mission lifespans.
The technology supports NASA’s broader objectives, including the search for ancient microbial life. By enabling faster and safer traversal to scientifically significant sites, such as Jezero Crater’s delta, the AI enhances the rovers’ ability to collect and analyze samples for future return to Earth.
Collaborative Innovation
Developed in partnership with tech giants and academic institutions, AutoNav 2.0 integrates open-source AI frameworks and custom algorithms tailored for space. The system is lightweight to accommodate the rovers’ limited computational resources, yet robust enough to operate in Mars’ harsh environment, where temperatures can plummet to -140°C and radiation poses constant threats.
NASA has also open-sourced portions of the AI codebase, inviting global developers to contribute to future iterations. This move aligns with NASA’s commitment to fostering innovation in space exploration, with potential applications for lunar missions and beyond.
A New Frontier for Space AI
The success of AutoNav 2.0 marks a pivotal moment for AI in space exploration. NASA plans to deploy similar neural network systems on upcoming missions, including the Europa Clipper and Dragonfly rotorcraft for Titan. “AI is transforming how we explore the cosmos,” said JPL Director Dr. Michael Watkins. “It’s not just about reaching Mars—it’s about exploring smarter, faster, and farther than ever before.”
As NASA continues to push the boundaries of autonomous exploration, the integration of neural networks signals a new era of discovery, bringing humanity closer to unraveling the mysteries of the Red Planet and beyond.