Huawei Unveils CloudMatrix 384 AI System to Challenge Nvidia’s Dominance
Huawei Technologies debuted its cutting-edge AI computing system, CloudMatrix 384, at the World Artificial Intelligence Conference (WAIC) in Shanghai, positioning it as a direct competitor to Nvidia’s flagship GB200 NVL72. Powered by 384 Ascend 910C chips, the system marks a significant step in Huawei’s ambition to capture a leading share of China’s booming AI market, fueled by U.S. export restrictions on advanced Nvidia chips.
A Bold Leap in AI Hardware
The CloudMatrix 384 leverages Huawei’s proprietary “supernode” architecture, enabling high-speed chip interconnectivity that delivers nearly double the throughput of Nvidia’s GB200 NVL72 in certain metrics, according to industry analysts at Semi Analysis. While individual Ascend 910C chips may trail Nvidia’s B200 in raw power, Huawei compensates with system-level innovations, integrating more chips to achieve superior performance. This design allows the system to handle complex AI workloads, including training trillion-parameter models and supporting inference for large-scale applications.
Huawei Cloud CEO Zhang Pingan announced that the CloudMatrix 384 is already operational on Huawei’s cloud platform, serving clients like state-owned telecommunications firms and AI developers, including ByteDance. The system’s full-optical links and enhanced software stack, CANN, aim to rival Nvidia’s CUDA ecosystem, offering a robust alternative for Chinese enterprises.
Navigating U.S. Export Controls
The development follows U.S. restrictions that blocked Nvidia’s H100 and B200 chips from the Chinese market, creating a void Huawei is eager to fill. The Ascend 910C, an evolution of the 910B, doubles the computing power and memory capacity of its predecessor, with added support for diverse AI workloads. Huawei began mass shipments of the 910C in May 2025, with over 800,000 chips already distributed to domestic customers, according to Reuters. The upcoming Ascend 910D, currently in testing, aims to surpass Nvidia’s H100 in performance, with samples expected by late May 2025.
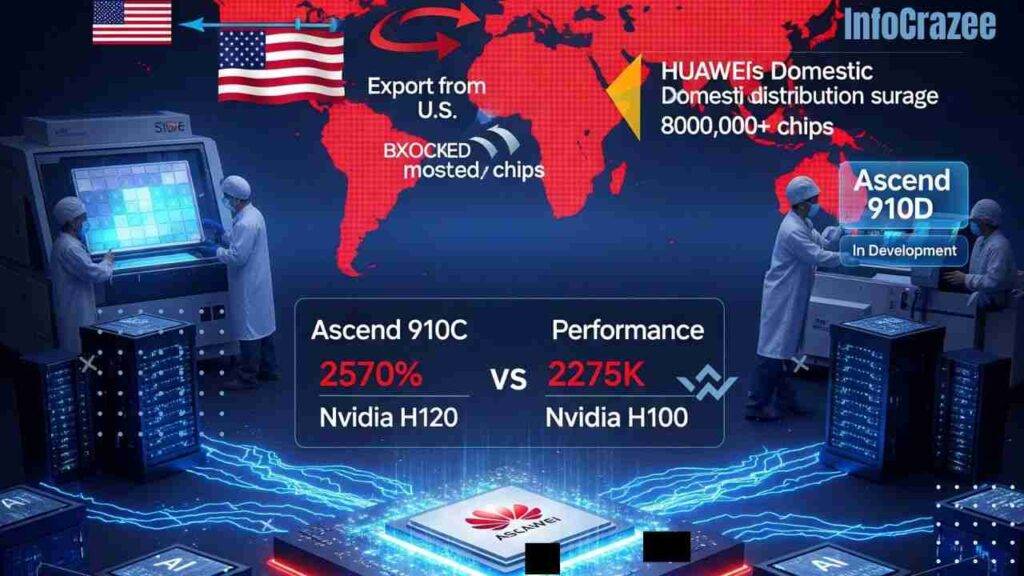
Despite challenges, including lower chip yields from China’s SMIC using 7nm process technology, Huawei’s strategic push has drawn global attention. Analyst Paul Triolo from Albright Stonebridge Group noted that the 910C has become the “hardware of choice” for Chinese AI developers, especially after tightened U.S. export curbs on Nvidia’s H20 chip.
Market Implications
The unveiling sparked a 2% drop in Nvidia’s stock on July 25, 2025, reflecting investor concerns about Huawei’s growing competitiveness in a market where China accounts for significant data center revenue. While Nvidia’s CUDA software remains a benchmark, Huawei’s CANN is gaining traction, supported by its open-source availability and compatibility with domestic hardware.
Industry experts, including Neil Shah from Counterpoint Research, acknowledge Huawei’s progress but note that Nvidia leads in software orchestration and ecosystem maturity. However, Huawei’s focus on system-level design and scalability positions it as a formidable player, especially in China’s $7 billion AI chip market.
A New Era of Competition
Huawei’s CloudMatrix 384 underscores China’s push for semiconductor self-sufficiency amid geopolitical tensions. With ongoing investments in R&D and partnerships with local tech giants like Baidu, Huawei is not only challenging Nvidia but also reshaping the global AI hardware landscape. As testing of the Ascend 910D progresses, the tech world awaits results that could further intensify this high-stakes rivalry.