Your morning commute takes exactly 23 minutes—not because you left earlier, but because traffic lights coordinated perfectly, adjusting in real-time to traffic flow. Your bus arrived precisely on schedule, tracked by an app that told you exactly when to leave home. The air quality is excellent today because sensors detected pollution spikes overnight and adjusted traffic patterns automatically.
This isn’t science fiction. It’s Copenhagen, Singapore, Barcelona—cities that are already “smart.”
Welcome to the era where technology is transforming urban centers from passive environments into intelligent, responsive systems that adapt to their residents’ needs. Smart cities aren’t a distant dream—they’re being built right now, and the pace is accelerating faster than most people realize.
What Makes a City “Smart”?
A smart city uses digital technology, data analytics, and connected devices (the Internet of Things) to improve quality of life, reduce resource consumption, and make urban services more efficient.
Key characteristics:
Connected infrastructure: Traffic systems, utilities, public transport, and emergency services all share data and coordinate actions.
Data-driven decisions: City managers use real-time information rather than guesswork to solve problems.
Citizen engagement: Residents interact with city services through apps, providing feedback and accessing information instantly.
Sustainability focus: Smart systems reduce energy consumption, waste, and emissions while improving livability.
Think of it as giving a city a nervous system, a brain, and the ability to learn.
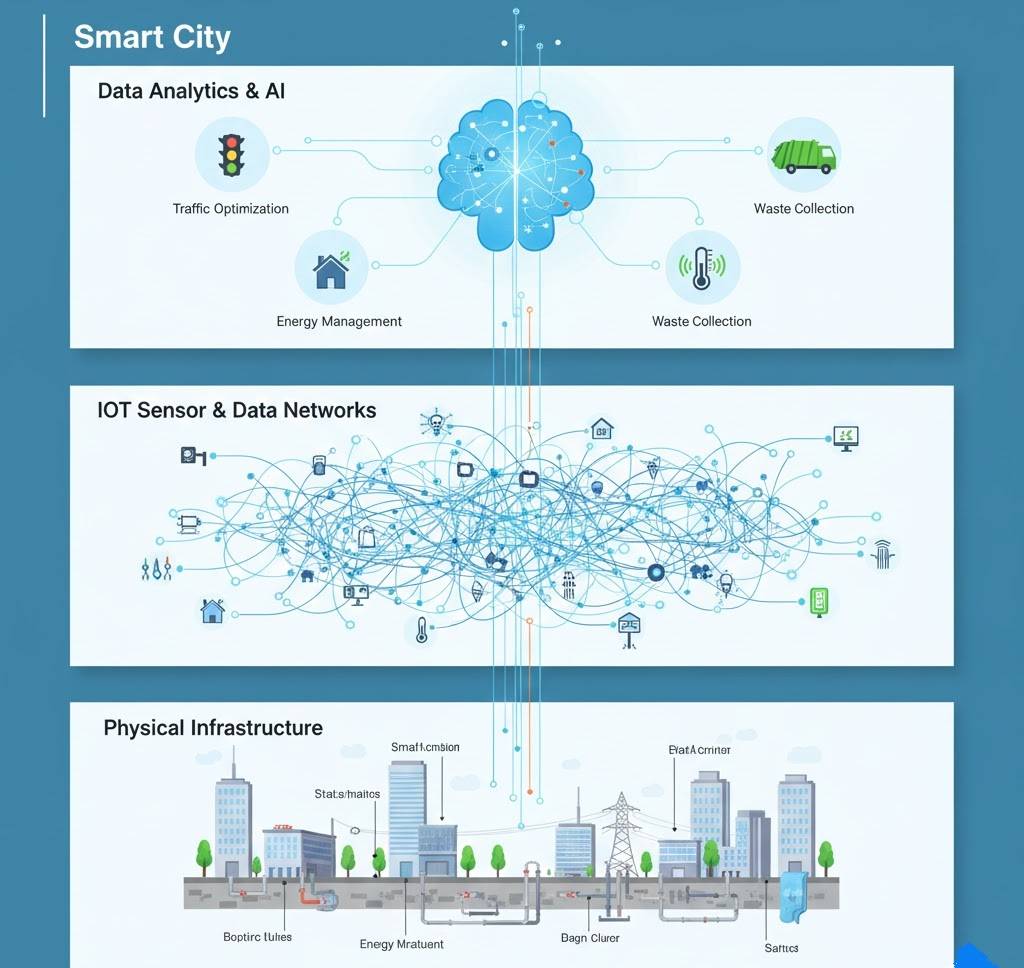
The Technologies Driving the Revolution
Several key technologies are converging to make smart cities possible:
5G Networks: The Foundation
5G connectivity provides the bandwidth and low latency needed for millions of devices to communicate instantly. A smart city might have sensors on every streetlight, trash can, parking space, and building—all transmitting data continuously.
What 5G enables:
- Autonomous vehicles communicating with infrastructure
- Real-time video monitoring and analysis
- Instant emergency response coordination
- Remote surgery in city hospitals
- AR/VR city services and navigation
Cities like Seoul, Shanghai, and London are blanketing their urban cores with 5G infrastructure, creating the foundation for everything else.
Internet of Things (IoT): The Sensors Everywhere
IoT sensors are the eyes and ears of smart cities, monitoring:
Air quality: Detecting pollution sources and triggering responses Traffic flow: Counting vehicles, identifying congestion patterns Water systems: Finding leaks, monitoring quality, tracking usage Waste management: Signaling when bins need emptying Energy consumption: Identifying inefficiencies building-by-building Structural health: Monitoring bridges, buildings for safety issues

Barcelona has over 20,000 sensors throughout the city. Singapore’s network is even more comprehensive. These cities know what’s happening everywhere, all the time.
Artificial Intelligence: The Decision Maker
AI systems process torrents of data from IoT sensors, identifying patterns humans couldn’t spot and making split-second decisions:
Predicting traffic: Not just reacting to congestion but preventing it Optimizing energy grids: Balancing supply and demand in real-time Detecting crime patterns: Alerting police to emerging problems Forecasting maintenance needs: Fixing infrastructure before it fails Managing emergencies: Coordinating resources during disasters
In Los Angeles, AI reduced traffic congestion by 12% just by optimizing traffic light timing citywide.
Big Data Analytics: Understanding Patterns
Smart cities generate enormous data streams—petabytes daily. Big data analytics transform this raw information into actionable insights:
- Which neighborhoods need more public transit?
- Where should we plant trees to maximize cooling?
- What times do different areas need more police presence?
- How can we reduce water waste across the city?

Cities like Dubai use advanced analytics platforms that integrate dozens of data sources, giving planners unprecedented insight into urban dynamics.
Digital Twins: Virtual City Replicas
Perhaps most fascinating: cities are creating digital twins—complete virtual replicas where planners can test changes before implementing them physically.
How it works:
- Create detailed 3D model of entire city
- Feed it real-time data from actual city
- Simulate proposed changes (new transit line, building development, traffic pattern modification)
- See projected impacts before spending a dollar on construction
Singapore has a comprehensive digital twin called “Virtual Singapore.” Planners tested evacuation routes, solar panel placements, and new development impacts all in the virtual realm first.
Real-World Transformations Happening Now
Let’s look at what’s actually being built:
Copenhagen: The Sustainable Smart City
Copenhagen aims for carbon neutrality by 2025. Technology enables this:
Smart street lighting: LED lights that brighten when people approach, dim when empty, saving 60% energy.
Integrated mobility: One app covers bikes, buses, trains, car-sharing—making car ownership unnecessary.
District heating: AI optimizes heat distribution through underground pipes, using waste heat from electricity generation.
Result: Carbon emissions dropped 38% while population and economy grew.
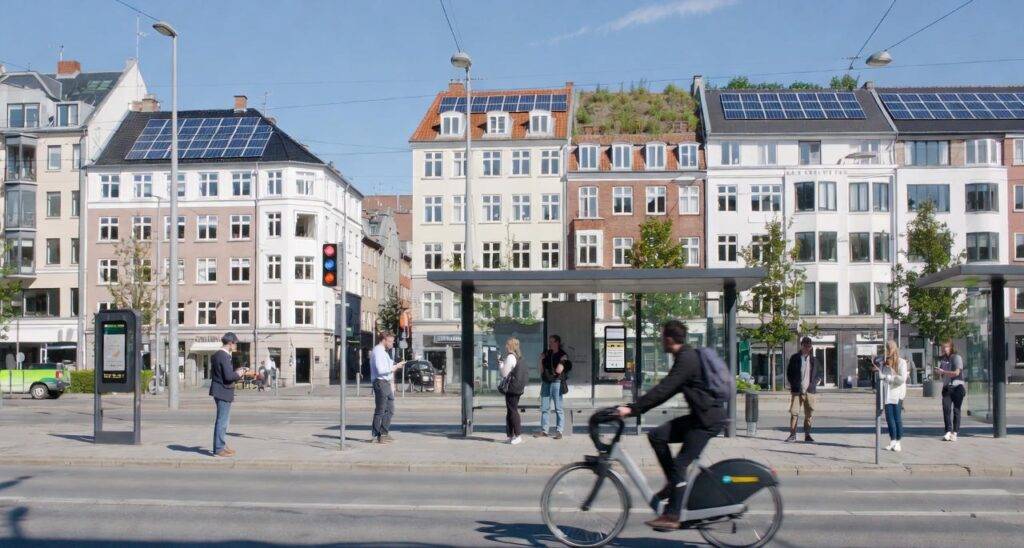

Singapore: The Comprehensive Smart Nation
Singapore’s “Smart Nation” initiative is arguably the world’s most comprehensive:
Autonomous vehicles: Testing self-driving buses and taxis on public roads.
Smart homes: Government housing equipped with sensors monitoring elderly residents’ wellbeing, alerting family if something’s wrong.
Cashless payments: Nearly eliminating physical money through digital systems.
Predictive maintenance: Sensors on elevators predict failures before they occur.
Water management: AI optimizes the world’s most advanced water recycling system.
Barcelona: The Citizen-Centric Model
Barcelona focuses on using technology to improve residents’ lives directly:
Smart parking: Sensors guide drivers to available spaces, reducing traffic by 30% in pilot areas.
Waste collection: Sensors trigger collection only when bins are full, reducing truck trips by 40%.
Digital democracy: Decidim platform lets citizens propose and vote on city projects—over 40,000 people participate regularly.
Public WiFi: Free citywide internet access as a public utvility.

Songdo, South Korea: Built Smart from Scratch
Unlike retrofitting existing cities, Songdo was designed as smart from the ground up:
Underground logistics: Waste automatically transported through tubes—no garbage trucks.
Pervasive sensors: Everything monitored—temperature, energy use, traffic, air quality.
Central control: City operations managed from unified command center.
Sustainable design: LEED-certified buildings, 40% green space, renewable energy.
The challenge: Creating community in a city that sometimes feels more efficient than human. Residents report it’s impressively functional but lacks the organic character of traditional cities.
The Benefits: Why Cities Are Racing to Become Smart
The advantages are compelling:
Environmental Sustainability
Energy efficiency: Smart grids reduce waste by 15-20%.
Emissions reduction: Optimized traffic cuts pollution significantly.
Water conservation: Leak detection and smart irrigation save millions of gallons.
Waste reduction: Smart collection and recycling increase rates by 30%+.
Economic Growth
Attracting talent: Tech workers prefer smart cities.
Business efficiency: Companies benefit from better infrastructure and data access.
Innovation ecosystems: Smart cities become hubs for tech startups.
Cost savings: Cities save billions through efficiency improvements.
Quality of Life
Reduced commute times: AI-optimized traffic saves hours weekly.
Better healthcare: Telemedicine and predictive health monitoring.
Increased safety: Smart policing reduces crime rates.
Cleaner environment: Real-time pollution management improves health.

The Challenges: It’s Not All Seamless
Smart city development faces significant obstacles:
Privacy Concerns
Surveillance worries: When everything is monitored, where’s the line between public safety and invasive tracking?
Cities are addressing this through:
- Strict data governance policies
- Anonymization techniques
- Transparent reporting on data usage
- Citizen oversight boards
Cybersecurity Risks
A connected city is a vulnerable city. Hackers could theoretically:
- Disrupt traffic systems
- Compromise power grids
- Access private data
- Create chaos during emergencies
Robust cybersecurity is essential but expensive and complex.
Digital Divide
Not everyone benefits equally. Smart city services require:
- Smartphones or computers
- Digital literacy
- Internet access
- Comfort with technology
Cities must ensure elderly residents, low-income populations, and technologically hesitant citizens aren’t left behind.
Cost and Complexity
Initial investment is enormous: Billions in infrastructure, sensors, networks, and systems.
Smaller cities struggle to afford comprehensive smart city development, creating a technology gap between wealthy and poor urban areas.

The Global Race: Who’s Leading?
Top smart cities globally (2025):
- Singapore: Most comprehensive integration
- Copenhagen: Sustainability leadership
- Zurich: Quality of life focus
- Amsterdam: Citizen participation
- Seoul: Technological innovation
- Barcelona: Social impact
- London: Data analytics
- San Francisco: Tech ecosystem
- Dubai: Ambitious vision
- Tokyo: Scale and efficiency
Rapidly emerging smart cities:
- Shenzhen, China: Tech manufacturing hub becoming smart showcase
- Tallinn, Estonia: Digital government pioneer
- Helsinki, Finland: Open data leader
- Kigali, Rwanda: Leapfrogging to smart infrastructure
The Future: What’s Coming Next
Smart city technology continues evolving rapidly:
Autonomous Everything (2025-2030)
- Self-driving cars becoming standard
- Drone delivery networks citywide
- Autonomous public transit
- Robotic maintenance and cleaning
AI City Managers (2028-2035)
- AI systems making routine city decisions independently
- Predictive governance anticipating problems
- Real-time resource allocation optimization
- Digital mayors coordinating with human leaders
Climate Adaptation (Ongoing)
- Smart systems helping cities adapt to climate change
- Flood prediction and prevention
- Heat island mitigation
- Renewable energy optimization

Hyperconnectivity (2030+)
- 6G networks enabling even more data
- Brain-computer interfaces for direct city interaction
- Holographic city services
- Fully immersive digital-physical integration
Getting It Right: Lessons Learned
Successful smart cities share common principles:
Start with problems, not technology: Identify actual issues residents face, then apply technology—not the reverse.
Engage citizens: Residents must be partners, not just users. Barcelona’s success stems from extensive community involvement.
Protect privacy: Trust requires transparent data policies and meaningful safeguards.
Build incrementally: Copenhagen didn’t become smart overnight. Start with pilot projects, learn, expand.
Ensure equity: Design systems accessible to everyone, regardless of age, income, or technical skill.
Plan for failure: Systems will malfunction. Have backups and manual alternatives.
Your Role in the Smart City Future
Even if you’re not a city planner or technologist, you’re part of this transformation:
Provide feedback: Use city apps, report issues, participate in digital democracy platforms.
Adopt smart services: The more residents use smart systems, the better they work.
Demand accountability: Ensure your city is using technology responsibly and equitably.
Stay informed: Understand what data your city collects and how it’s used.
Vote: Support leaders who prioritize both smart innovation and citizen welfare.

The Promise and the Challenge
Smart cities represent humanity’s best attempt to make urban life sustainable, efficient, and pleasant as billions more people move to cities in coming decades.
Technology can reduce traffic, clean the air, save energy, improve safety, and connect communities. But it can also surveil, exclude, and dehumanize if implemented without wisdom and care.
The cities getting it right balance innovation with humanity. They remember that technology is a tool, not a goal—that the point is serving people, not impressing them with gadgets.
As more cities become “smart,” the question isn’t whether this transformation will continue—it’s whether we’ll ensure the smart cities we build are also wise, just, and truly livable.
The future of urban life is being coded right now. Let’s make sure we get the algorithm right.





