The sun doesn’t shine at night. The wind doesn’t blow on schedule. Rain doesn’t fall when reservoirs run low. For decades, these simple facts were renewable energy’s greatest weakness.
Then we taught computers to predict the unpredictable, optimize the chaotic, and coordinate what seemed impossibly complex. Machine learning didn’t just improve renewable energy—it made the impossible possible.
This is the story of how artificial intelligence is solving the puzzle that stumped humanity for generations: how to power civilization entirely from sources that won’t cooperate.
The Renewable Energy Problem
Before we understand the solution, let’s understand why renewable energy was so difficult.
Traditional power generation was predictable. Coal plants, natural gas facilities, and nuclear reactors produce steady, controllable power. Need more electricity? Burn more fuel. Need less? Dial it back. Simple.
Renewable sources are fundamentally different:
Solar panels only work when the sun shines—and that varies by clouds, seasons, time of day, air quality, and weather patterns. Wind turbines depend on air currents that shift unpredictably. Hydroelectric dams require water flow that varies with rainfall. Tidal energy follows the moon. Geothermal is location-specific.
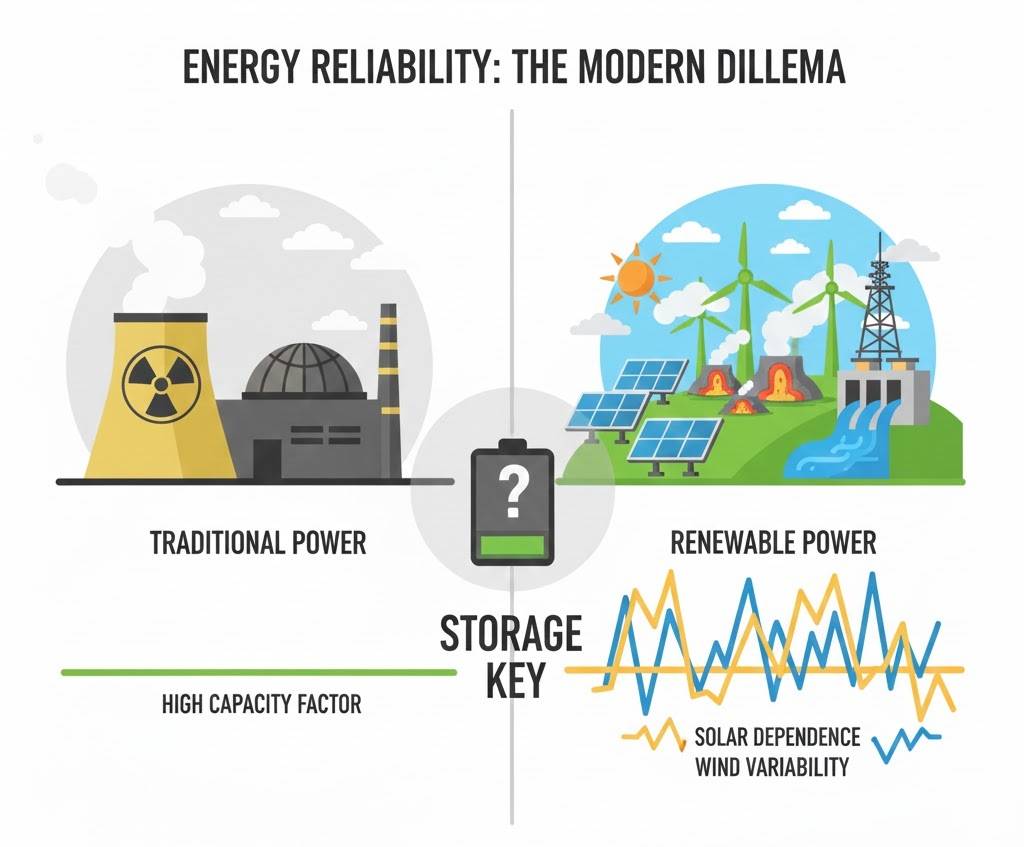
Worse, electricity demand also fluctuates wildly—morning coffee surge, midday industrial peak, evening cooking and entertainment spike. Matching chaotic supply with chaotic demand? That was the impossible puzzle.
Until machine learning changed everything.
Predicting the Unpredictable: Weather Forecasting Revolution
Machine learning’s first breakthrough was making renewable sources predictable.
Traditional weather forecasting used physics equations and human meteorologist expertise. Useful, but imprecise. Solar and wind operators needed to know: exactly how much power will we generate in the next hour, tomorrow, next week?
Machine learning transformed this completely.
AI systems now analyze:
- Satellite imagery (updated every few minutes)
- Historical weather patterns (decades of data)
- Ocean temperatures and currents
- Atmospheric pressure systems
- Seasonal patterns and climate trends
- Local geographic factors
- Real-time sensor data from thousands of stations
The algorithms spot patterns humans never could, predicting solar generation 48 hours ahead with 95% accuracy and wind production 72 hours out with 90% accuracy.

Real-world impact: A wind farm in Texas knows three days in advance when production will drop, allowing grid operators to arrange backup sources. Solar installations in California predict tomorrow’s output within 2% accuracy, enabling precise grid planning.
Predictability transformed renewable energy from unreliable to dependable.
Smart Grids: The Orchestrated Dance
Knowing what’s coming is only half the solution. Machine learning also coordinates the complex ballet of matching supply with demand second-by-second.
Modern smart grids use ML algorithms to manage thousands of energy sources simultaneously:
Every solar panel, wind turbine, battery storage facility, and backup generator communicates with the central AI. The system knows instantaneously:
- Current production from each source
- Current demand across the entire grid
- Battery storage levels
- Predicted production for next hours/days
- Predicted demand patterns
- Equipment status and maintenance needs
The AI makes millions of micro-decisions per second: Route solar from Arizona to California. Charge batteries in Texas while wind is strong. Release stored energy in New York during evening peak. Activate backup generation in specific locations. Adjust industrial customer usage through demand response programs.
The result? Grids now handle 80%+ renewable energy without blackouts—something considered impossible twenty years ago.
Optimizing Individual Installations
Machine learning doesn’t just coordinate grids—it makes each individual renewable installation dramatically more efficient.
Solar farms: ML algorithms control panel angles, adjusting throughout the day to capture maximum sunlight. They predict optimal cleaning schedules, detect failing panels before they break, and identify shade patterns that reduce efficiency.
One California solar farm increased output by 12% using ML optimization—the equivalent of adding hundreds of panels without installing any.
Wind turbines: AI adjusts blade pitch thousands of times daily, optimizing for current wind conditions. It predicts mechanical stress, scheduling maintenance before failures occur. It coordinates turbine groups so they don’t interfere with each other’s airflow.
Offshore wind farms using ML produce 20% more power than identical farms without AI optimization.

Hydroelectric dams: Machine learning predicts rainfall patterns, optimizes water release timing, and balances electricity generation with irrigation, flood control, and environmental needs. The algorithms manage competing demands that would overwhelm human operators.
Energy Storage: Solving the Time-Shift Problem
Solar produces too much during midday, nothing at night. Wind blows strongest when demand is lowest. Storage solves this, but only if managed intelligently.
Battery management systems powered by ML determine:
- When to charge (during excess production, low electricity prices)
- When to discharge (during peak demand, high prices)
- How much capacity to reserve for emergencies
- Degradation rates and lifespan optimization
- Temperature management for maximum efficiency
These decisions must account for weather forecasts, electricity price fluctuations, grid conditions, and battery chemistry—all simultaneously.
Tesla’s Hornsdale Power Reserve in Australia uses ML to respond to grid instabilities in milliseconds, preventing blackouts and earning millions by selling stored energy at optimal times. The system has prevented multiple state-wide outages.

Demand Response: The Other Side of the Equation
Machine learning doesn’t just manage supply—it shapes demand.
Smart demand response systems communicate with millions of devices:
Your smart thermostat receives a signal: “Solar production is peaking, electricity is cheap and abundant right now.” It pre-cools your home by 2°F, storing cold for later. You never notice, but you’ve helped balance the grid.
Scale this to millions of homes, plus:
- Electric vehicles charging when renewable energy peaks
- Industrial facilities scheduling energy-intensive processes during high production
- Data centers moving computing tasks to times/locations with renewable surplus
- Water heaters, pool pumps, and appliances operating during optimal windows
The system learns: When do people accept temperature adjustments? What charging delays are tolerable? Which industrial processes are flexible?

Result: Demand curves smooth out, matching renewable supply patterns better. Grid stress decreases. Costs drop.
Economic Optimization: The Profit Motive
Machine learning makes renewable energy economically superior, not just environmentally.
Energy trading algorithms operate in electricity markets, buying and selling power in real-time:
- Predict price fluctuations based on weather, demand patterns, and market conditions
- Arbitrage opportunities: buy electricity when cheap, store, sell when expensive
- Optimize asset deployment: which turbines/panels to operate given current prices
- Balance long-term contracts with spot market opportunities
Some renewable installations now generate more revenue from intelligent trading than from pure electricity production.
Manufacturing optimization: ML predicts equipment failures before they happen, schedules maintenance during low-production periods, and optimizes supply chains for replacement parts.

Downtime in wind farms dropped 40% using predictive maintenance. Solar installations catch defects months earlier. Efficiency gains directly improve profitability.
Environmental Intelligence
Beyond economics, ML helps renewables minimize their own environmental impact.
Wildlife protection: Cameras and ML algorithms detect approaching birds or bats near wind turbines, temporarily stopping blades to prevent collisions. Mortality rates dropped 70% in installations using this technology.
Ecosystem monitoring: AI analyzes how hydroelectric operations affect downstream ecosystems, optimizing release schedules to protect fish populations while maintaining power generation.
Material efficiency: ML optimizes manufacturing processes for solar panels and wind turbines, reducing waste and improving recyclability.
The Grid of Tomorrow
Looking ahead, ML is enabling innovations that seemed like fantasy:
Virtual power plants aggregate thousands of home batteries, solar panels, and EVs, coordinating them as one massive power source that can replace traditional plants.
Microgrids use ML to operate independently during disasters, intelligently managing local renewable sources to keep communities powered when main grids fail.
Cross-continental coordination allows European wind power to supplement Asian solar, with ML managing the complexity of time zones, regulations, and infrastructure.

The Human Element
Despite AI’s dominance, humans remain essential:
Engineers design the systems ML optimizes. Grid operators oversee AI decisions and intervene during unusual situations. Policymakers create frameworks ensuring ML serves public interest. Researchers develop better algorithms and identify new applications.
AI makes humans more effective—it doesn’t replace human judgment, creativity, and values.
The Climate Impact
Machine learning’s impact on renewable energy translates directly to climate action:
Global renewable capacity has tripled since ML-optimized systems became standard. Cost per kilowatt-hour from solar and wind has dropped 85%. Grid reliability with high renewable penetration has improved dramatically.
Result: Renewable energy is now cheaper than fossil fuels in most markets, accelerating the transition to clean energy and reducing global emissions faster than predicted.

The Revolution Continues
Machine learning hasn’t finished transforming renewable energy—it’s just beginning.
Future applications include:
- Fusion energy management requiring AI to control plasma
- Space-based solar coordinating orbital power stations
- Ocean current harvesting optimized by ML
- Artificial photosynthesis guided by learning algorithms
The renewable energy revolution wasn’t just about new technology—it was about making that technology smart enough to work with nature’s complexity rather than against it.
Machine learning gave us the intelligence to harness chaos, coordinate complexity, and power civilization from sources that once seemed too unreliable to trust.
The sun still doesn’t shine at night. But now, we’re ready when it rises.





